ABP成长系列7:数据访问
2024-06-01 16:01:56一、仓储
仓储模式是ABP框架数据访问层的核心抽象,它提供了一种统一的方式来访问数据源,无论底层使用何种数据库技术(EF Core、MongoDB等)。
- 接口抽象:框架定义了一系列通用的仓储接口,如 IRepository<TEntity, TKey>。你的领域层和应用层只依赖于这些接口,而不是具体的实现,这严格遵循了DDD的持久化无关原则。
- 默认实现:ABP为EF、MongoDB和Dapper提供了这些仓储接口的开箱即用的实现。这意味着对于大多数标准的CRUD操作,无需编写任何仓储实现代码。
- 自定义仓储:对于复杂的查询或特定操作,可以定义自定义的仓储接口(如 ICustomRepository),并在基础设施层(如EntityFrameworkCore项目)中实现它。ABP的依赖注入系统会自动将其注册到容器中。
类关系图
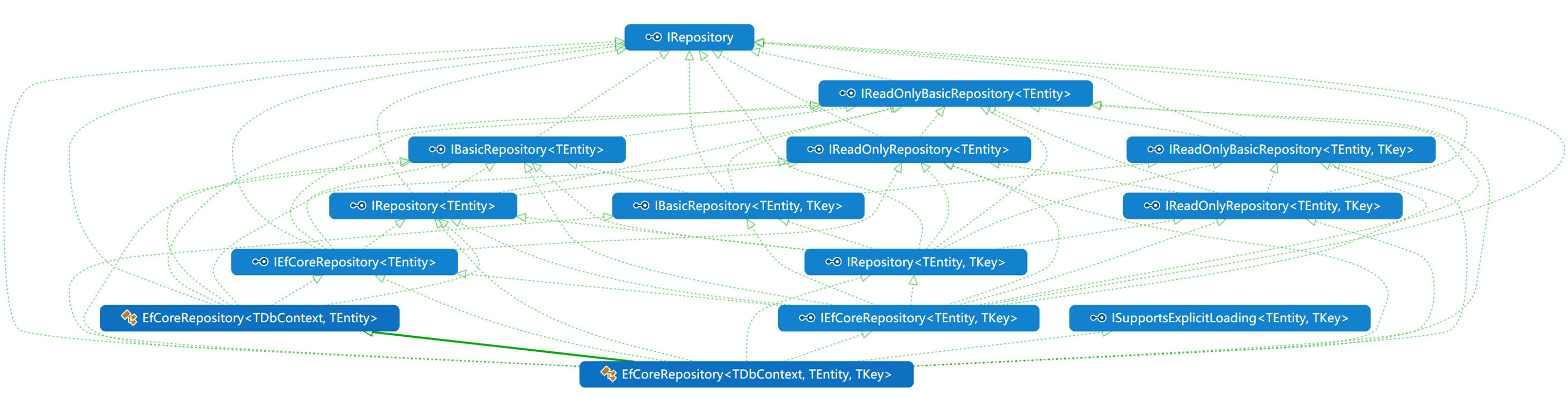
1. 仓储接口体系
ABP定义了一套完整的仓储接口体系,位于Volo.Abp.Domain.Repositories命名空间:
//IRepository.cs
public interface IRepository { }
public interface IRepository<TEntity> : IReadOnlyRepository<TEntity>, IBasicRepository<TEntity>
where TEntity : class, IEntity
{
Task<TEntity> FindAsync([NotNull] Expression<Func<TEntity, bool>> predicate, bool includeDetails = true, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default);
Task<TEntity> GetAsync([NotNull] Expression<Func<TEntity, bool>> predicate, bool includeDetails = true, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default);
Task DeleteAsync([NotNull] Expression<Func<TEntity, bool>> predicate, bool autoSave = false, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default
);
}
public interface IRepository<TEntity, TKey> : IRepository<TEntity>, IReadOnlyRepository<TEntity, TKey>, IBasicRepository<TEntity, TKey>
where TEntity : class, IEntity<TKey> { }
//IBasicRepository.cs
public interface IBasicRepository<TEntity> : IReadOnlyBasicRepository<TEntity>
where TEntity : class, IEntity
{
[NotNull]
Task<TEntity> InsertAsync([NotNull] TEntity entity, bool autoSave = false, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default);
Task InsertManyAsync([NotNull] IEnumerable<TEntity> entities, bool autoSave = false, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default);
[NotNull]
Task<TEntity> UpdateAsync([NotNull] TEntity entity, bool autoSave = false, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default);
Task UpdateManyAsync([NotNull] IEnumerable<TEntity> entities, bool autoSave = false, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default);
Task DeleteAsync([NotNull] TEntity entity, bool autoSave = false, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default);
Task DeleteManyAsync([NotNull] IEnumerable<TEntity> entities, bool autoSave = false, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default);
}
public interface IBasicRepository<TEntity, TKey> : IBasicRepository<TEntity>, IReadOnlyBasicRepository<TEntity, TKey>
where TEntity : class, IEntity<TKey>
{
Task DeleteAsync(TKey id, bool autoSave = false, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default);
Task DeleteManyAsync([NotNull] IEnumerable<TKey> ids, bool autoSave = false, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default);
}
//IReadOnlyRepository.cs
public interface IReadOnlyRepository<TEntity> : IReadOnlyBasicRepository<TEntity> where TEntity : class, IEntity
{
IAsyncQueryableExecuter AsyncExecuter { get; }
[Obsolete("Use WithDetailsAsync method.")]
IQueryable<TEntity> WithDetails();
[Obsolete("Use WithDetailsAsync method.")]
IQueryable<TEntity> WithDetails(params Expression<Func<TEntity, object>>[] propertySelectors);
Task<IQueryable<TEntity>> WithDetailsAsync(); //TODO: CancellationToken
Task<IQueryable<TEntity>> WithDetailsAsync(params Expression<Func<TEntity, object>>[] propertySelectors); //TODO: CancellationToken
Task<IQueryable<TEntity>> GetQueryableAsync(); //TODO: CancellationToken
/// <summary>
/// Gets a list of entities by the given <paramref name="predicate"/>.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="predicate">A condition to filter the entities</param>
/// <param name="includeDetails">Set true to include details (sub-collections) of this entity</param>
/// <param name="cancellationToken">A <see cref="T:System.Threading.CancellationToken" /> to observe while waiting for the task to complete.</param>
Task<List<TEntity>> GetListAsync(
[NotNull] Expression<Func<TEntity, bool>> predicate,
bool includeDetails = false,
CancellationToken cancellationToken = default);
}
public interface IReadOnlyRepository<TEntity, TKey> : IReadOnlyRepository<TEntity>, IReadOnlyBasicRepository<TEntity, TKey>
where TEntity : class, IEntity<TKey> { }
//IReadOnlyBasicRepository.cs
public interface IReadOnlyBasicRepository<TEntity> : IRepository where TEntity : class, IEntity
{
Task<List<TEntity>> GetListAsync(bool includeDetails = false, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default);
Task<long> GetCountAsync(CancellationToken cancellationToken = default);
Task<List<TEntity>> GetPagedListAsync(
int skipCount,
int maxResultCount,
string sorting,
bool includeDetails = false,
CancellationToken cancellationToken = default);
}
public interface IReadOnlyBasicRepository<TEntity, TKey> : IReadOnlyBasicRepository<TEntity>
where TEntity : class, IEntity<TKey>
{
[NotNull]
Task<TEntity> GetAsync(TKey id, bool includeDetails = true, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default);
Task<TEntity> FindAsync(TKey id, bool includeDetails = true, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default);
}
2. 核心:动态注册
ABP使用依赖注入系统动态提供仓储实现。当你在应用层或领域服务中注入IRepository
- 动态注册:在模块的ConfigureServices方法中,ABP会调用AddDefaultRepositories来注册默认仓储
services.AddAbpDbContext<MyDbContext>(options =>
{
options.AddDefaultRepositories(includeAllEntities: true);
});
其核心实现位于 Volo.Abp.EntityFrameworkCore.AbpDbContextRegistrationOptions
public AbpDbContextRegistrationOptions AddDefaultRepositories(bool includeAllEntities = false)
{
foreach (var entityType in GetEntityTypes(_dbContextType))
{
if (!includeAllEntities && !typeof(IAggregateRoot).IsAssignableFrom(entityType))
{
continue;
}
var repositoryType = typeof(IRepository<>).MakeGenericType(entityType);
if (!_serviceCollection.IsRegistered(repositoryType))
{
var implType = typeof(EfCoreRepository<,>)
.MakeGenericType(_dbContextType, entityType);
_serviceCollection.AddTransient(repositoryType, implType);
}
}
return this;
}
3. 核心:ABP扩展
ABP提供了许多有用的仓储扩展方法,位于 Volo.Abp.Domain.Repositories 命名空间
public static class RepositoryExtensions
{
public static async Task EnsureCollectionLoadedAsync<TEntity, TKey, TProperty>(
this IBasicRepository<TEntity, TKey> repository,
TEntity entity,
Expression<Func<TEntity, IEnumerable<TProperty>>> propertyExpression,
CancellationToken cancellationToken = default
)
where TEntity : class, IEntity<TKey>
where TProperty : class
{
var repo = ProxyHelper.UnProxy(repository) as ISupportsExplicitLoading<TEntity, TKey>;
if (repo != null)
{
await repo.EnsureCollectionLoadedAsync(entity, propertyExpression, cancellationToken);
}
}
public static async Task EnsurePropertyLoadedAsync<TEntity, TKey, TProperty>(
this IBasicRepository<TEntity, TKey> repository,
TEntity entity,
Expression<Func<TEntity, TProperty>> propertyExpression,
CancellationToken cancellationToken = default
)
where TEntity : class, IEntity<TKey>
where TProperty : class
{
var repo = ProxyHelper.UnProxy(repository) as ISupportsExplicitLoading<TEntity, TKey>;
if (repo != null)
{
await repo.EnsurePropertyLoadedAsync(entity, propertyExpression, cancellationToken);
}
}
public static async Task HardDeleteAsync<TEntity>(
this IRepository<TEntity> repository,
Expression<Func<TEntity, bool>> predicate,
bool autoSave = false,
CancellationToken cancellationToken = default
)
where TEntity : class, IEntity, ISoftDelete
{
var uowManager = repository.GetUnitOfWorkManager();
if (uowManager.Current == null)
{
using (var uow = uowManager.Begin())
{
await HardDeleteWithUnitOfWorkAsync(repository, predicate, autoSave, cancellationToken, uowManager.Current);
await uow.CompleteAsync(cancellationToken);
}
}
else
{
await HardDeleteWithUnitOfWorkAsync(repository, predicate, autoSave, cancellationToken, uowManager.Current);
}
}
public static async Task HardDeleteAsync<TEntity>(
this IBasicRepository<TEntity> repository,
IEnumerable<TEntity> entities,
bool autoSave = false,
CancellationToken cancellationToken = default
)
where TEntity : class, IEntity, ISoftDelete
{
var uowManager = repository.GetUnitOfWorkManager();
if (uowManager.Current == null)
{
using (var uow = uowManager.Begin())
{
await HardDeleteWithUnitOfWorkAsync(repository, entities, autoSave, cancellationToken, uowManager.Current);
await uow.CompleteAsync(cancellationToken);
}
}
else
{
await HardDeleteWithUnitOfWorkAsync(repository, entities, autoSave, cancellationToken, uowManager.Current);
}
}
public static async Task HardDeleteAsync<TEntity>(
this IBasicRepository<TEntity> repository,
TEntity entity,
bool autoSave = false,
CancellationToken cancellationToken = default
)
where TEntity : class, IEntity, ISoftDelete
{
var uowManager = repository.GetUnitOfWorkManager();
if (uowManager.Current == null)
{
using (var uow = uowManager.Begin())
{
await HardDeleteWithUnitOfWorkAsync(repository, entity, autoSave, cancellationToken, uowManager.Current);
await uow.CompleteAsync(cancellationToken);
}
}
else
{
await HardDeleteWithUnitOfWorkAsync(repository, entity, autoSave, cancellationToken, uowManager.Current);
}
}
private static IUnitOfWorkManager GetUnitOfWorkManager<TEntity>(
this IBasicRepository<TEntity> repository,
[CallerMemberName] string callingMethodName = nameof(GetUnitOfWorkManager)
)
where TEntity : class, IEntity
{
if (ProxyHelper.UnProxy(repository) is not IUnitOfWorkManagerAccessor unitOfWorkManagerAccessor)
{
throw new AbpException($"The given repository (of type {repository.GetType().AssemblyQualifiedName}) should implement the " +
$"{typeof(IUnitOfWorkManagerAccessor).AssemblyQualifiedName} interface in order to invoke the {callingMethodName} method!");
}
if (unitOfWorkManagerAccessor.UnitOfWorkManager == null)
{
throw new AbpException($"{nameof(unitOfWorkManagerAccessor.UnitOfWorkManager)} property of the given {nameof(repository)} object is null!");
}
return unitOfWorkManagerAccessor.UnitOfWorkManager;
}
private static async Task HardDeleteWithUnitOfWorkAsync<TEntity>(
IRepository<TEntity> repository,
Expression<Func<TEntity, bool>> predicate,
bool autoSave,
CancellationToken cancellationToken,
IUnitOfWork currentUow
)
where TEntity : class, IEntity, ISoftDelete
{
using (currentUow.ServiceProvider.GetRequiredService<IDataFilter<ISoftDelete>>().Disable())
{
var entities = await repository.AsyncExecuter.ToListAsync((await repository.GetQueryableAsync()).Where(predicate), cancellationToken);
await HardDeleteWithUnitOfWorkAsync(repository, entities, autoSave, cancellationToken, currentUow);
}
}
private static async Task HardDeleteWithUnitOfWorkAsync<TEntity>(
IBasicRepository<TEntity> repository,
IEnumerable<TEntity> entities,
bool autoSave,
CancellationToken cancellationToken,
IUnitOfWork currentUow
)
where TEntity : class, IEntity, ISoftDelete
{
var hardDeleteEntities = (HashSet<IEntity>)currentUow.Items.GetOrAdd(
UnitOfWorkItemNames.HardDeletedEntities,
() => new HashSet<IEntity>()
);
hardDeleteEntities.UnionWith(entities);
await repository.DeleteManyAsync(entities, autoSave, cancellationToken);
}
private static async Task HardDeleteWithUnitOfWorkAsync<TEntity>(
IBasicRepository<TEntity> repository,
TEntity entity,
bool autoSave,
CancellationToken cancellationToken,
IUnitOfWork currentUow
)
where TEntity : class, IEntity, ISoftDelete
{
var hardDeleteEntities = (HashSet<IEntity>)currentUow.Items.GetOrAdd(
UnitOfWorkItemNames.HardDeletedEntities,
() => new HashSet<IEntity>()
);
hardDeleteEntities.Add(entity);
await repository.DeleteAsync(entity, autoSave, cancellationToken);
}
}
4. 核心:异步执行与取消
ABP仓储的所有方法都支持异步操作和取消令牌
public virtual async Task UpdateManyAsync(IEnumerable<TEntity> entities, bool autoSave = false, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
foreach (var entity in entities)
{
await UpdateAsync(entity, cancellationToken: cancellationToken);
}
if (autoSave)
{
await SaveChangesAsync(cancellationToken);
}
}
二、工作单元
类关系图
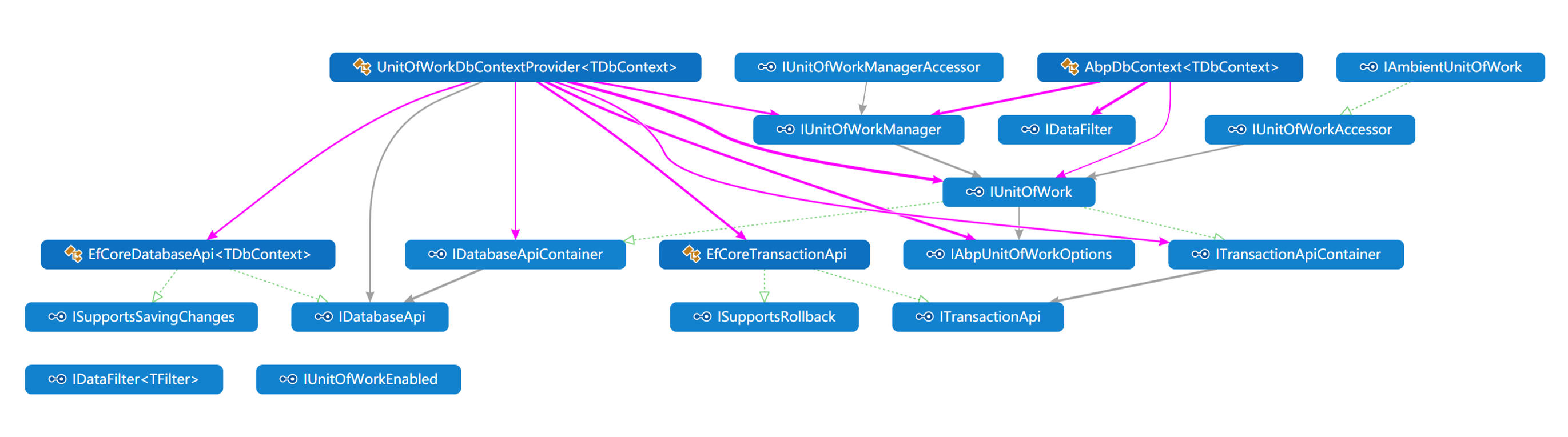
1. 机制
- 自动工作单元:通过 [UnitOfWork] 特性标记方法
- 手动工作单元:通过注入 IUnitOfWorkManager 手动控制
public class BookAppService : ApplicationService
{
private readonly IUnitOfWorkManager _unitOfWorkManager;
public BookAppService(IUnitOfWorkManager unitOfWorkManager)
{
_unitOfWorkManager = unitOfWorkManager;
}
public async Task CreateAsync(CreateBookDto input)
{
using (var uow = _unitOfWorkManager.Begin())
{
var book = new Book { Name = input.Name };
await _bookRepository.InsertAsync(book);
await uow.CompleteAsync();
}
}
}
数据库事务行为
- HTTP GET请求不会启动事务性UOW,它们仍然启动UOW,但不创建数据库事务。
- 如果底层数据库提供程序支持数据库事务,那么所有其他HTTP请求类型都使用数据库事务启动UOW。
2. 工作单元的事务控制
- 通过 [UnitOfWork] 特性的属性控制事务行为
[UnitOfWork(
IsDisabled = false, // 是否禁用工作单元
IsTransactional = true, // 是否启用事务
Timeout = 30, // 超时时间(秒)
IsolationLevel = IsolationLevel.ReadCommitted // 隔离级别
)]
public async Task UpdateBookAsync(Guid id, UpdateBookDto input)
{
// 方法实现...
}
- 事务API:ABP定义了 ITransactionApi 接口来抽象不同数据库的事务
public interface ITransactionApi : IDisposable
{
Task CommitAsync(CancellationToken cancellationToken = default);
Task RollbackAsync(CancellationToken cancellationToken = default);
}
3. 嵌套工作单元
ABP支持嵌套工作单元,内部工作单元可以继承或覆盖外部工作单元的配置
[UnitOfWork(IsTransactional = true)]
public async Task OuterMethod()
{
// 外部工作单元
await _repository.InsertAsync(new Entity());
// 内部工作单元默认继承外部工作单元的事务
await InnerMethod();
// 可以显式创建新工作单元
using (var uow = _unitOfWorkManager.Begin(requiresNew: true))
{
await _repository.InsertAsync(new Entity());
await uow.CompleteAsync();
}
}
[UnitOfWork(IsTransactional = false)]
public async Task InnerMethod()
{
// 此方法覆盖了外部工作单元的IsTransactional设置
await _repository.InsertAsync(new Entity());
}
4. 事件系统
ABP工作单元提供了完整的事件通知机制
public class MyService : ITransientDependency
{
private readonly IUnitOfWorkManager _unitOfWorkManager;
public MyService(IUnitOfWorkManager unitOfWorkManager)
{
_unitOfWorkManager = unitOfWorkManager;
// 订阅工作单元事件
_unitOfWorkManager.Current.OnCompleted += OnUowCompleted;
_unitOfWorkManager.Current.OnFailed += OnUowFailed;
_unitOfWorkManager.Current.OnDisposed += OnUowDisposed;
}
private void OnUowCompleted(object sender, UnitOfWorkEventArgs e)
{
Logger.LogInformation($"Unit of work {e.UnitOfWork.Id} completed");
}
private void OnUowFailed(object sender, UnitOfWorkFailedEventArgs e)
{
Logger.LogError(e.Exception, $"Unit of work {e.UnitOfWork.Id} failed");
}
private void OnUowDisposed(object sender, UnitOfWorkEventArgs e)
{
Logger.LogInformation($"Unit of work {e.UnitOfWork.Id} disposed");
}
}
**5. 核心1:IUnitOfWork **
public interface IUnitOfWork : IDatabaseApiContainer, ITransactionApiContainer, IDisposable
{
// 工作单元唯一标识
Guid Id { get; }
// 工作单元选项
IUnitOfWorkOptions Options { get; }
// 外部工作单元(用于嵌套工作单元)
IUnitOfWork Outer { get; }
// 是否已释放
bool IsDisposed { get; }
// 是否已完成
bool IsCompleted { get; }
// 工作单元事件
event EventHandler<UnitOfWorkEventArgs> OnCompleted;
event EventHandler<UnitOfWorkFailedEventArgs> OnFailed;
event EventHandler<UnitOfWorkEventArgs> OnDisposed;
// 工作单元操作方法
void Initialize(UnitOfWorkOptions options);
Task SaveChangesAsync(CancellationToken cancellationToken = default);
Task CompleteAsync(CancellationToken cancellationToken = default);
Task RollbackAsync(CancellationToken cancellationToken = default);
// 添加/获取数据库API
void AddDatabaseApi(IDatabaseApi databaseApi);
IDatabaseApi GetDatabaseApi();
// 添加/获取事务API
void AddTransactionApi(ITransactionApi transactionApi);
ITransactionApi GetTransactionApi();
// 添加/获取特性
void AddFeature(string key, object value);
TFeature GetFeature<TFeature>(string key);
}
6. 核心2:UnitOfWorkManager
UnitOfWorkManager负责创建工作单元实例和管理当前工作单元
- Begin
- Current
public class UnitOfWorkManager : IUnitOfWorkManager, ISingletonDependency
{
// 当前工作单元
public IUnitOfWork Current => _currentUow.Value;
// 创建工作单元
public IUnitOfWork Begin(UnitOfWorkOptions options, bool requiresNew = false)
{
// 如果不需要新工作单元且已有当前工作单元,则返回null(由内部处理嵌套)
if (!requiresNew && _currentUow.Value != null)
{
return new ChildUnitOfWork(_currentUow.Value);
}
// 创建新工作单元
var unitOfWork = _unitOfWork.CreateNew();
unitOfWork.Initialize(options);
// 设置当前工作单元
_currentUow.Value = unitOfWork;
return unitOfWork;
}
// 其他方法...
}
7: 核心3:UseUnitOfWork
ABP使用UseUnitOfWork在ASP.NET Core项目中集成工作单元模式,也就是启动了一个AbpUnitOfWorkMiddleware中间件
public static IApplicationBuilder UseUnitOfWork(this IApplicationBuilder app)
{
return app
.UseAbpExceptionHandling()
.UseMiddleware<AbpUnitOfWorkMiddleware>();
}
public class AbpUnitOfWorkMiddleware : IMiddleware, ITransientDependency
{
private readonly IUnitOfWorkManager _unitOfWorkManager;
private readonly AbpAspNetCoreUnitOfWorkOptions _options;
public AbpUnitOfWorkMiddleware(
IUnitOfWorkManager unitOfWorkManager,
IOptions<AbpAspNetCoreUnitOfWorkOptions> options)
{
_unitOfWorkManager = unitOfWorkManager;
_options = options.Value;
}
public async Task InvokeAsync(HttpContext context, RequestDelegate next)
{
if (IsIgnoredUrl(context))
{
await next(context);
return;
}
using (var uow = _unitOfWorkManager.Reserve(UnitOfWork.UnitOfWorkReservationName))
{
await next(context);
await uow.CompleteAsync(context.RequestAborted);
}
}
private bool IsIgnoredUrl(HttpContext context)
{
return context.Request.Path.Value != null &&
_options.IgnoredUrls.Any(x => context.Request.Path.Value.StartsWith(x));
}
}
三、数据过滤
1. 内置数据过滤器
- 软删除(ISoftDelete):自动过滤已删除的实体
- 多租户(IMultiTenant):自动按租户ID过滤数据
2. 核心1:核心接口
public interface IDataFilter
{
IDisposable Enable<TFilter>() where TFilter : class;
IDisposable Disable<TFilter>() where TFilter : class;
bool IsEnabled<TFilter>() where TFilter : class;
}
3. 核心2:EF的实现
// 源码位置:Volo.Abp.EntityFrameworkCore.AbpDbContext.cs
protected override Expression<Func<TEntity, bool>> CreateFilterPredicate<TEntity>()
{
var predicate = base.CreateFilterPredicate<TEntity>();
// 软删除过滤
if (typeof(ISoftDelete).IsAssignableFrom(typeof(TEntity))
&& DataFilter?.IsEnabled<ISoftDelete>() == true)
{
Expression<Func<TEntity, bool>> softDeleteFilter = e => !EF.Property<bool>(e, "IsDeleted");
predicate = predicate == null
? softDeleteFilter
: QueryFilterExpressionHelper.CombineExpressions(predicate, softDeleteFilter);
}
// 多租户过滤
if (typeof(IMultiTenant).IsAssignableFrom(typeof(TEntity))
&& DataFilter?.IsEnabled<IMultiTenant>() == true)
{
var tenantId = CurrentTenant.Id;
Expression<Func<TEntity, bool>> multiTenantFilter = e => EF.Property<Guid>(e, "TenantId") == tenantId;
predicate = predicate == null
? multiTenantFilter
: QueryFilterExpressionHelper.CombineExpressions(predicate, multiTenantFilter);
}
return predicate;
}
4. 核心3:MongoDb的实现
// 源码位置:Volo.Abp.MongoDB.AbpMongoDbRepository.cs
protected virtual FilterDefinition<TEntity> CreateFilterDefinition()
{
var filters = new List<FilterDefinition<TEntity>>();
// 软删除过滤
if (typeof(ISoftDelete).IsAssignableFrom(typeof(TEntity))
&& DataFilter?.IsEnabled<ISoftDelete>() == true)
{
filters.Add(Builders<TEntity>.Filter.Eq(x => ((ISoftDelete)x).IsDeleted, false));
}
// 多租户过滤
if (typeof(IMultiTenant).IsAssignableFrom(typeof(TEntity))
&& DataFilter?.IsEnabled<IMultiTenant>() == true)
{
filters.Add(Builders<TEntity>.Filter.Eq(x => ((IMultiTenant)x).TenantId, CurrentTenant.Id));
}
return filters.Count > 0
? Builders<TEntity>.Filter.And(filters)
: FilterDefinition<TEntity>.Empty;
}
EF和MongoDb的实现逻辑不一样,EF是在AbpDbContext中,而MongoDb是在仓储中。
4. 自定义过滤器:数据权限
现在,我们来实现一个自定义的数据过滤器,实现数据权限控制:管理员可以查看所有数据,普通用户只能查看自己的数据。
- 定义数据权限接口
public interface IDataPermissionFilter
{
// 这是一个标记接口,用于标识数据权限过滤器
}
public interface IHasOwner
{
Guid? OwnerId { get; }
}
- 实现数据权限过滤器提供者
public class MyDbContext : AbpDbContext<MyDbContext>
{
public DbSet<Book> Books { get; set; }
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder builder)
{
base.OnModelCreating(builder);
builder.Entity<Book>(b =>
{
b.Property(x => x.OwnerId).HasColumnName("OwnerId");
});
}
protected override Expression<Func<TEntity, bool>> CreateFilterPredicate<TEntity>()
{
var predicate = base.CreateFilterPredicate<TEntity>();
// 添加数据权限过滤
if (typeof(IHasOwner).IsAssignableFrom(typeof(TEntity))
&& DataFilter?.IsEnabled<IDataPermissionFilter>() == true)
{
var currentUserId = CurrentUser.Id;
if (!CurrentUser.IsInRole("admin") && currentUserId.HasValue)
{
Expression<Func<TEntity, bool>> dataPermissionFilter =
e => EF.Property<Guid?>(e, "OwnerId") == currentUserId;
predicate = predicate == null
? dataPermissionFilter
: QueryFilterExpressionHelper.CombineExpressions(predicate, dataPermissionFilter);
}
}
return predicate;
}
}
- 实体上实现接口
public class Book : AggregateRoot<Guid>, IHasOwner
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public Guid? OwnerId { get; set; } // 实现IHasOwner接口
}
- 使用数据过滤器
public class BookAppService : ApplicationService
{
private readonly IRepository<Book, Guid> _bookRepository;
private readonly IDataFilter _dataFilter;
public BookAppService(IRepository<Book, Guid> bookRepository, IDataFilter dataFilter)
{
_bookRepository = bookRepository;
_dataFilter = dataFilter;
}
// 普通查询会自动应用数据权限过滤
public async Task<List<BookDto>> GetMyBooksAsync()
{
var books = await _bookRepository.GetListAsync();
return ObjectMapper.Map<List<Book>, List<BookDto>>(books);
}
// 管理员可以禁用过滤器查看所有数据
public async Task<List<BookDto>> GetAllBooksAsync()
{
using (_dataFilter.Disable<IDataPermissionFilter>())
{
var books = await _bookRepository.GetListAsync();
return ObjectMapper.Map<List<Book>, List<BookDto>>(books);
}
}
}
- 注册配置
[DependsOn(typeof(AbpDataModule))]
public class MyModule : AbpModule
{
public override void ConfigureServices(ServiceConfigurationContext context)
{
// 注册自定义DbContext
context.Services.AddAbpDbContext<MyDbContext>(options =>
{
options.AddDefaultRepositories();
});
}
}
扩展:与权限模块配合
protected override Expression<Func<TEntity, bool>> CreateFilterPredicate<TEntity>()
{
var predicate = base.CreateFilterPredicate<TEntity>();
if (typeof(IHasOwner).IsAssignableFrom(typeof(TEntity))
&& DataFilter?.IsEnabled<IDataPermissionFilter>() == true)
{
if (await PermissionChecker.IsGrantedAsync("AllDataPermission"))
{
// 有全部数据权限,不过滤
return predicate;
}
if (await PermissionChecker.IsGrantedAsync("DepartmentDataPermission"))
{
// 部门数据权限
var departmentIds = await GetUserDepartmentIdsAsync();
Expression<Func<TEntity, bool>> deptFilter =
e => departmentIds.Contains(EF.Property<Guid>(e, "DepartmentId"));
predicate = predicate == null
? deptFilter
: QueryFilterExpressionHelper.CombineExpressions(predicate, deptFilter);
}
else
{
// 默认只能查看自己的数据
var currentUserId = CurrentUser.Id;
if (currentUserId.HasValue)
{
Expression<Func<TEntity, bool>> ownerFilter =
e => EF.Property<Guid?>(e, "OwnerId") == currentUserId;
predicate = predicate == null
? ownerFilter
: QueryFilterExpressionHelper.CombineExpressions(predicate, ownerFilter);
}
else
{
// 未登录用户看不到任何数据
predicate = e => false;
}
}
}
return predicate;
}
四、数据提供者
1. EFCore类关系图
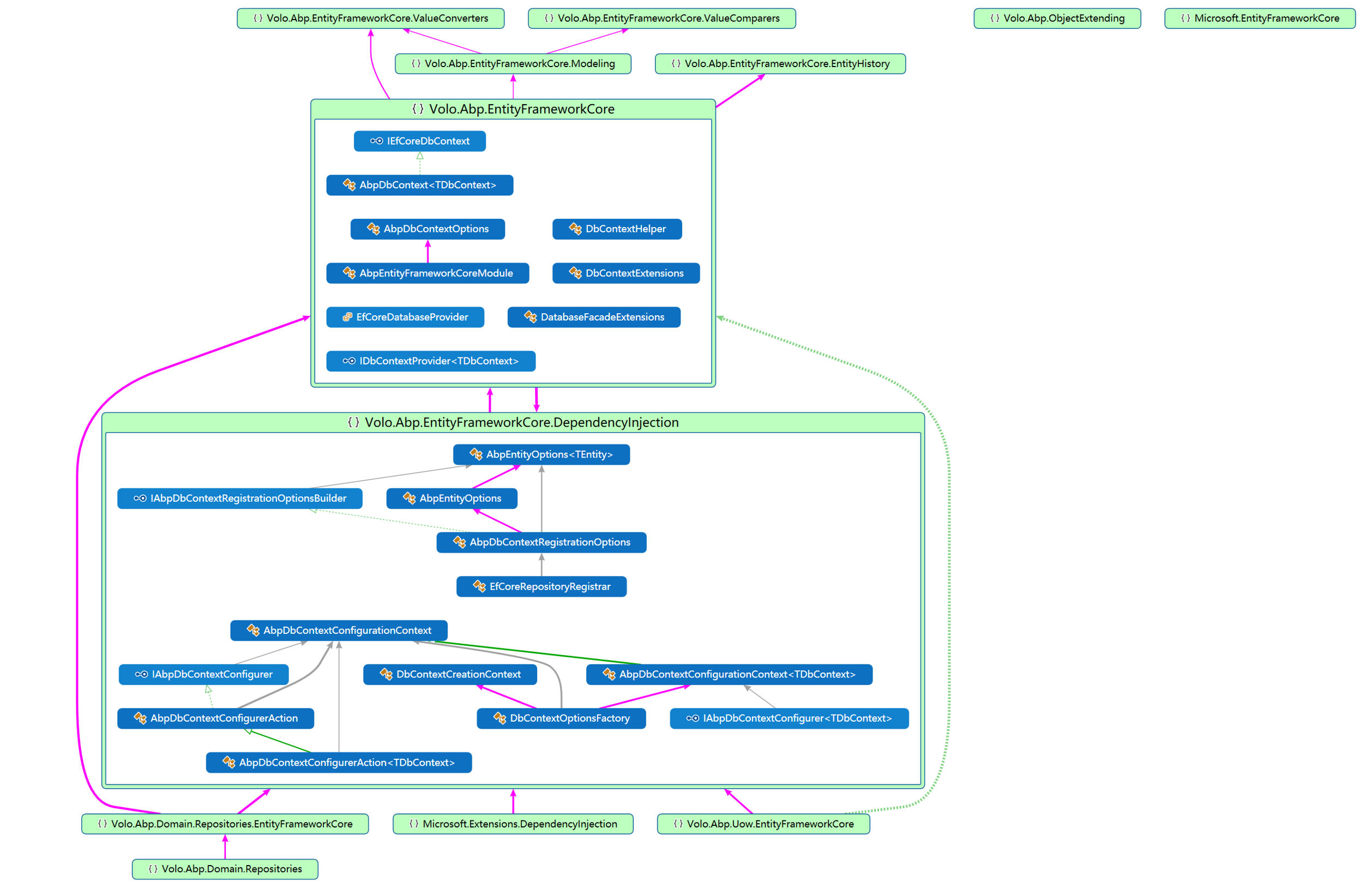
2. MongoDb类关系图
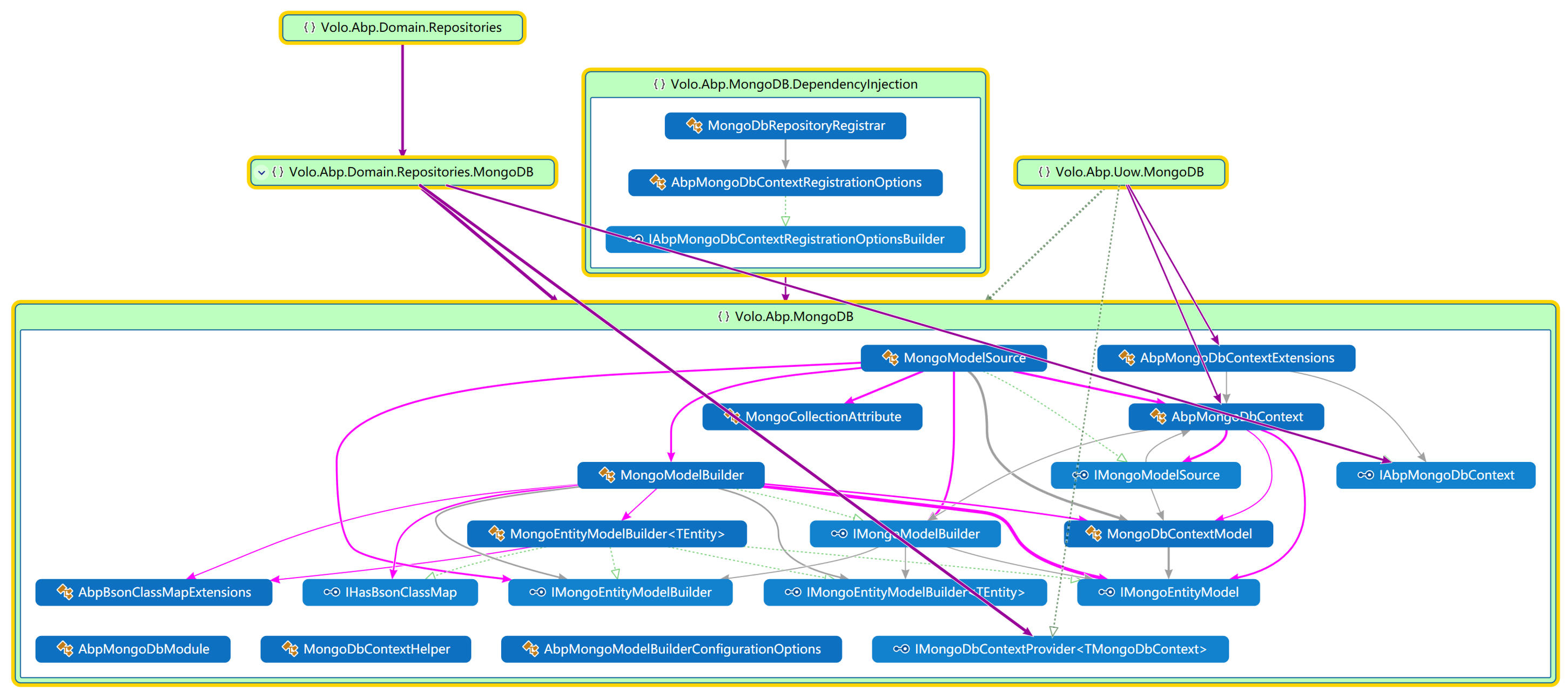
五、数据审计
ABP的数据审计系统是一个强大的功能,它能够自动记录实体变更历史,为系统提供完整的操作追踪能力。
类关系图
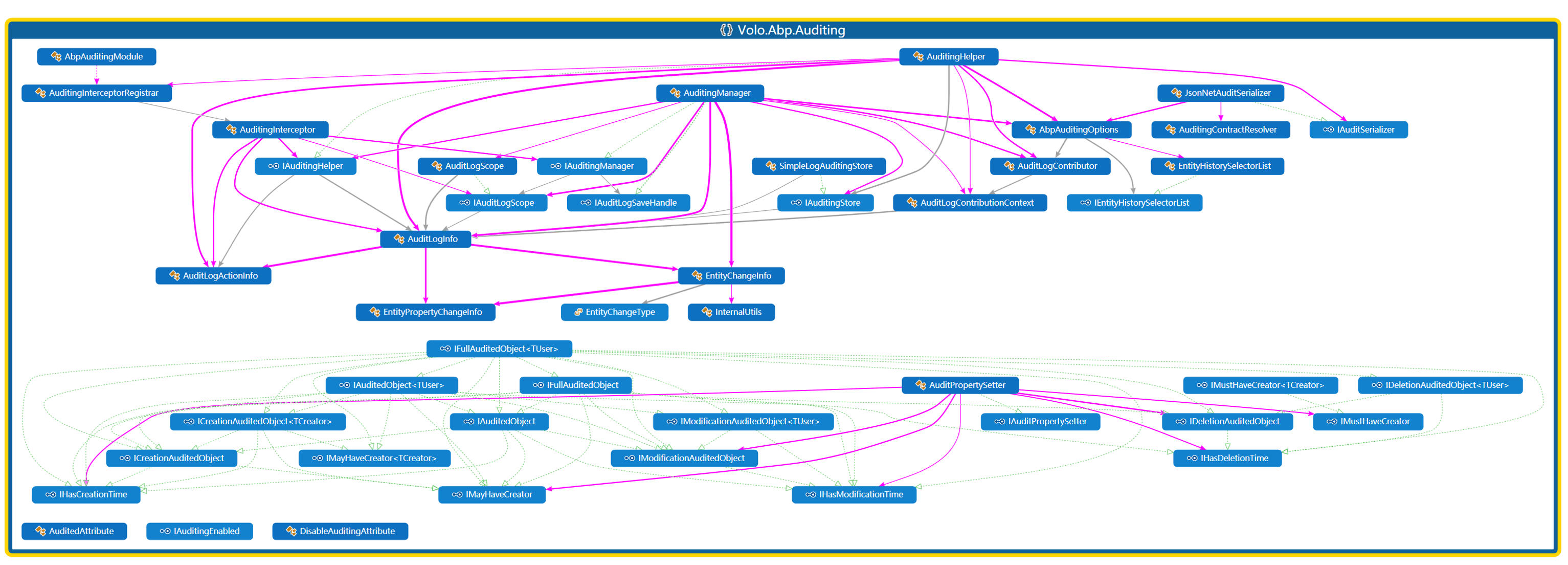
1. 审计系统核心架构
IAuditingManager:审计管理器的接口
AuditingManager:审计管理器的默认实现
IAuditingStore:审计存储接口
AuditLogInfo:审计日志的数据结构
AuditingInterceptor:AOP拦截器
2. 核心1:AuditingManager
AuditingManager 作为审计系统的"大脑",主要承担以下职责:
- 审计流程的启动与协调
- 审计日志的创建与组装
- 审计贡献者的调用执行
- 审计日志的最终提交
public class AuditingManager : IAuditingManager, ITransientDependency
{
private const string AmbientContextKey = "Volo.Abp.Auditing.IAuditLogScope";
protected IServiceProvider ServiceProvider { get; }
protected AbpAuditingOptions Options { get; }
protected ILogger<AuditingManager> Logger { get; set; }
private readonly IAmbientScopeProvider<IAuditLogScope> _ambientScopeProvider;
private readonly IAuditingHelper _auditingHelper;
private readonly IAuditingStore _auditingStore;
public AuditingManager(
IAmbientScopeProvider<IAuditLogScope> ambientScopeProvider,
IAuditingHelper auditingHelper,
IAuditingStore auditingStore,
IServiceProvider serviceProvider,
IOptions<AbpAuditingOptions> options)
{
ServiceProvider = serviceProvider;
Options = options.Value;
Logger = NullLogger<AuditingManager>.Instance;
_ambientScopeProvider = ambientScopeProvider;
_auditingHelper = auditingHelper;
_auditingStore = auditingStore;
}
public IAuditLogScope Current => _ambientScopeProvider.GetValue(AmbientContextKey);
public IAuditLogSaveHandle BeginScope()
{
// 1. 创建基础审计日志信息
_auditingHelper.CreateAuditLogInfo()
// 2. 创建审计作用域
var auditLogScope = new AuditLogScope(auditLogInfo);
// 3. 注册到环境作用域提供者
var ambientScope = _ambientScopeProvider.BeginScope(
AmbientContextKey,
auditLogScope
);
Debug.Assert(Current != null, "Current != null");
// 4. 返回保存句柄
return new DisposableSaveHandle(this, ambientScope, Current.Log, Stopwatch.StartNew());
}
// 其他内部方法...
}
设计亮点
- 环境上下文管理:
- 使用 IAmbientScopeProvider 管理作用域
- 支持异步调用链中的上下文传递
- 延迟提交机制
- 通过 IAuditLogSaveHandle 控制提交时机
- 支持异常情况下的优雅处理
- 线程安全设计
- 通过作用域隔离保证并发安全
- 使用不可变对象(AuditLogInfo)避免竞态条件
3. 核心2:审计拦截器
位于 Volo.Abp.Auditing 命名空间下的 AuditingInterceptor 是审计系统的入口点:
public class AuditingInterceptor : AbpInterceptor, ITransientDependency
{
public override async Task InterceptAsync(IAbpMethodInvocation invocation)
{
using (var serviceScope = _serviceScopeFactory.CreateScope())
{
var auditingHelper = serviceScope.ServiceProvider.GetRequiredService<IAuditingHelper>();
var auditingOptions = serviceScope.ServiceProvider.GetRequiredService<IOptions<AbpAuditingOptions>>().Value;
if (!ShouldIntercept(invocation, auditingOptions, auditingHelper))
{
await invocation.ProceedAsync();
return;
}
var auditingManager = serviceScope.ServiceProvider.GetRequiredService<IAuditingManager>();
if (auditingManager.Current != null)
{
await ProceedByLoggingAsync(invocation, auditingHelper, auditingManager.Current);
}
else
{
var currentUser = serviceScope.ServiceProvider.GetRequiredService<ICurrentUser>();
await ProcessWithNewAuditingScopeAsync(invocation, auditingOptions, currentUser, auditingManager, auditingHelper);
}
}
}
}
4. 核心3:审计日志创建过程
AuditingHelper 类负责创建审计日志:
public virtual AuditLogInfo CreateAuditLogInfo()
{
var auditInfo = new AuditLogInfo
{
ApplicationName = Options.ApplicationName,
TenantId = CurrentTenant.Id,
TenantName = CurrentTenant.Name,
UserId = CurrentUser.Id,
UserName = CurrentUser.UserName,
ClientId = CurrentClient.Id,
CorrelationId = CorrelationIdProvider.Get(),
ExecutionTime = Clock.Now,
ImpersonatorUserId = CurrentUser.FindImpersonatorUserId(),
ImpersonatorUserName = CurrentUser.FindImpersonatorUserName(),
ImpersonatorTenantId = CurrentUser.FindImpersonatorTenantId(),
ImpersonatorTenantName = CurrentUser.FindImpersonatorTenantName(),
};
ExecutePreContributors(auditInfo);
return auditInfo;
}
protected virtual void ExecutePreContributors(AuditLogInfo auditLogInfo)
{
using (var scope = ServiceProvider.CreateScope())
{
var context = new AuditLogContributionContext(scope.ServiceProvider, auditLogInfo);
foreach (var contributor in Options.Contributors)
{
try
{
contributor.PreContribute(context);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Logger.LogException(ex, LogLevel.Warning);
}
}
}
}
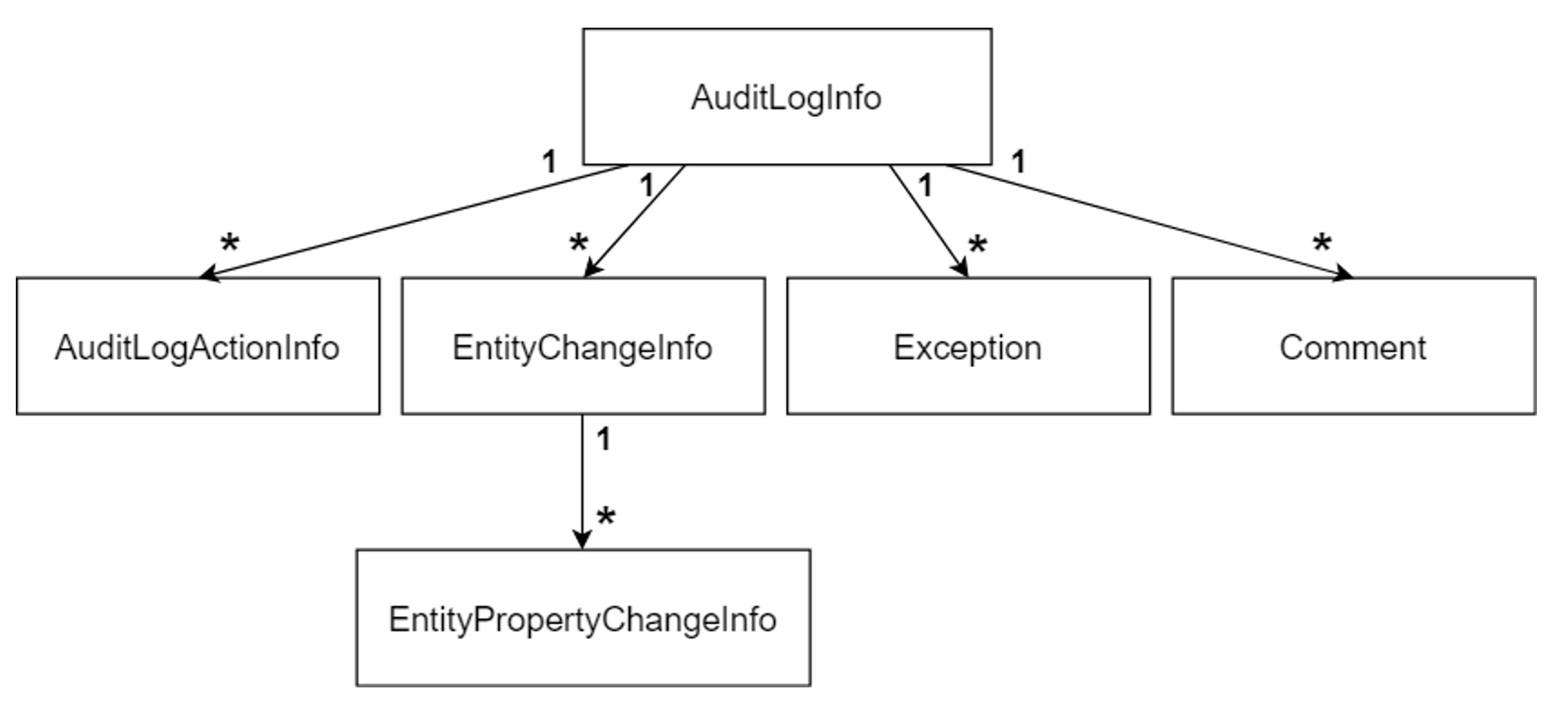
public class AuditLogInfo : IHasExtraProperties
{
public AuditLogInfo()
{
Actions = new List<AuditLogActionInfo>();
Exceptions = new List<Exception>();
ExtraProperties = new ExtraPropertyDictionary();
EntityChanges = new List<EntityChangeInfo>();
Comments = new List<string>();
}
// 其他代码
}
public class EntityChangeInfo
{
public List<EntityPropertyChangeInfo> PropertyChanges { get; set; }
// 其它代码
}
5. 实体变更审计
ABP 通过 Volo.Abp.EntityFrameworkCore.EntityHistory.EntityHistoryHelper 来跟踪实体的变更:
public class EntityHistoryHelper : IEntityHistoryHelper, ITransientDependency
{
public virtual List<EntityChangeInfo> CreateChangeList(ICollection<EntityEntry> entityEntries)
{
var list = new List<EntityChangeInfo>();
foreach (var entry in entityEntries)
{
if (!ShouldSaveEntityHistory(entry))
{
continue;
}
var entityChange = CreateEntityChangeOrNull(entry);
if (entityChange == null)
{
continue;
}
list.Add(entityChange);
}
return list;
}
[CanBeNull]
protected virtual EntityChangeInfo CreateEntityChangeOrNull(EntityEntry entityEntry)
{
var entity = entityEntry.Entity;
EntityChangeType changeType;
switch (entityEntry.State)
{
case EntityState.Added:
changeType = EntityChangeType.Created;
break;
case EntityState.Deleted:
changeType = EntityChangeType.Deleted;
break;
case EntityState.Modified:
changeType = IsDeleted(entityEntry) ? EntityChangeType.Deleted : EntityChangeType.Updated;
break;
case EntityState.Detached:
case EntityState.Unchanged:
default:
return null;
}
var entityId = GetEntityId(entity);
if (entityId == null && changeType != EntityChangeType.Created)
{
return null;
}
var entityType = entity.GetType();
var entityChange = new EntityChangeInfo
{
ChangeType = changeType,
EntityEntry = entityEntry,
EntityId = entityId,
EntityTypeFullName = entityType.FullName,
PropertyChanges = GetPropertyChanges(entityEntry),
EntityTenantId = GetTenantId(entity)
};
return entityChange;
}
}
6. 审计存储机制
ABP 提供了默认的审计存储实现 SimpleLogAuditingStore,但通常我们会实现自己的存储:
[Dependency(TryRegister = true)]
public class SimpleLogAuditingStore : IAuditingStore, ISingletonDependency
{
public ILogger<SimpleLogAuditingStore> Logger { get; set; }
public SimpleLogAuditingStore()
{
Logger = NullLogger<SimpleLogAuditingStore>.Instance;
}
public Task SaveAsync(AuditLogInfo auditInfo)
{
Logger.LogInformation(auditInfo.ToString());
return Task.FromResult(0);
}
}
7. 审计日志处理流程
- 拦截阶段:AuditingInterceptor 拦截方法调用
- 日志创建:AuditingHelper 创建基础审计日志
- 贡献者处理:调用所有注册的 AuditLogContributor
- 实体变更检测:EntityHistoryHelper 检测实体变更
- 存储阶段:调用 IAuditingStore 实现存储日志
8. 自定义审计
ABP的审计系统非常强大,其 IAuditLogContributor 接口允许我们深度定制审计日志内容。下面我将通过一个库存管理模块示例,详细说明如何实现自定义审计贡献者。
假设我们有一个库存管理系统,需要详细记录以下信息到审计日志:
- 库存变更详情:包括商品ID、变更前库存、变更后库存、安全库存水平等。
- 业务操作上下文:如触发此次库存变更的订单号或调拨单号。
- 自定义业务标签:例如操作类型(如“采购入库”、“销售出库”、“盘点调整”)。
- 创建自定义 AuditLogContributor
public class InventoryAuditLogContributor : AuditLogContributor, ITransientDependency
{
public override Task ContributeAsync(AuditLogContributionContext context)
{
// 1. 获取当前审计日志信息
var auditLogInfo = context.AuditInfo;
// 2. 从当前作用域或静态访问器中获取自定义业务数据
// 这里假设我们有一个自定义的上下文提供者,用于在方法调用间传递业务数据
var inventoryChangeContext = InventoryChangeContext.Current;
if (inventoryChangeContext != null)
{
// 3. 将业务数据添加到审计日志的 ExtraProperties 字典中
auditLogInfo.ExtraProperties["ProductId"] = inventoryChangeContext.ProductId;
auditLogInfo.ExtraProperties["OldStockQuantity"] = inventoryChangeContext.OldQuantity;
auditLogInfo.ExtraProperties["NewStockQuantity"] = inventoryChangeContext.NewQuantity;
auditLogInfo.ExtraProperties["SafetyStockLevel"] = inventoryChangeContext.SafetyStockLevel;
auditLogInfo.ExtraProperties["ReferenceOrderNumber"] = inventoryChangeContext.ReferenceOrderNumber;
auditLogInfo.ExtraProperties["OperationType"] = inventoryChangeContext.OperationType;
// 4. (可选)你也可以直接添加到 Comments 或自定义结构
auditLogInfo.Comments.Add($"库存操作: {inventoryChangeContext.OperationType}. 订单参考: {inventoryChangeContext.ReferenceOrderNumber}");
}
return Task.CompletedTask;
}
}
- 创建上下文对象(用于传递业务数据)
我们需要一个方式来在方法执行过程中传递这些业务数据。可以使用 AsyncLocal 来实现一个简单的上下文作用域。
public class InventoryChangeContext
{
private static readonly AsyncLocal<InventoryChangeContext> _current = new AsyncLocal<InventoryChangeContext>();
public static InventoryChangeContext Current => _current.Value;
public static void SetCurrent(InventoryChangeContext context)
{
_current.Value = context;
}
public Guid ProductId { get; set; }
public int OldQuantity { get; set; }
public int NewQuantity { get; set; }
public int SafetyStockLevel { get; set; }
public string ReferenceOrderNumber { get; set; }
public string OperationType { get; set; } // 例如:"PurchaseIn", "SaleOut", "StocktakeAdjustment"
}
- 在应用服务方法中使用上下文
public class ProductAppService : ApplicationService, IProductAppService
{
private readonly IRepository<Product, Guid> _productRepository;
public ProductAppService(IRepository<Product, Guid> productRepository)
{
_productRepository = productRepository;
}
public async Task UpdateStockAsync(Guid productId, int newQuantity, string operationType, string referenceOrderNumber)
{
// 1. 获取当前商品
var product = await _productRepository.GetAsync(productId);
var oldQuantity = product.StockQuantity;
// 2. 创建并设置审计日志上下文
var auditContext = new InventoryChangeContext
{
ProductId = productId,
OldQuantity = oldQuantity,
NewQuantity = newQuantity,
SafetyStockLevel = product.SafetyStockLevel,
ReferenceOrderNumber = referenceOrderNumber,
OperationType = operationType
};
InventoryChangeContext.SetCurrent(auditContext); // 设置到AsyncLocal
try
{
// 3. 执行实际的业务操作(更新库存)
product.UpdateStock(newQuantity);
await _productRepository.UpdateAsync(product);
// 4. 审计日志将由拦截器自动捕获,并通过InventoryAuditLogContributor贡献自定义数据
}
finally
{
// 5. 清理上下文(重要!避免内存泄漏或数据污染后续操作)
InventoryChangeContext.SetCurrent(null);
}
}
}
- 注册依赖(通常无需手动注册)
由于 InventoryAuditLogContributor 实现了 ITransientDependency,ABP框架会自动将其注册到依赖注入容器中。审计系统在保存日志前会自动调用所有实现的 IAuditLogContributor。
- 检查效果
当 UpdateStockAsync 方法被调用后,审计日志的 ExtraProperties 字段将包含你添加的自定义数据。如果你使用的是ABP内置的审计日志模块,这些数据会以JSON格式保存在 AbpAuditLogs 表的 ExtraProperties 列中
// AbpAuditLogs 表 ExtraProperties 列的内容示例
{
"ProductId": "3fa85f64-5717-4562-b3fc-2c963f66afa6",
"OldStockQuantity": 100,
"NewStockQuantity": 80,
"SafetyStockLevel": 50,
"ReferenceOrderNumber": "SO-20230909-001",
"OperationType": "SaleOut"
}
9. 最佳实践
- 实现自定义的 IAuditingStore 将审计日志存储到数据库
- 对于高频操作的方法,考虑使用 [DisableAuditing] 特性
- 通过 AbpAuditingOptions 配置审计系统的行为
- 使用 AuditLogContributor 添加业务相关的审计信息

